Surgical Solutions: Exploring Hysterectomy As A PCOS Treatment
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome affects millions of women worldwide, often bringing challenges like irregular periods, hormonal...
Read MoreStarting a conversation with your gynecologist can feel personal, but asking the right questions helps you make informed decisions about your health. Whether it is your first visit or a routine checkup, knowing what to ask encourages trust and open communication. From menstrual patterns to menopause concerns, understanding what to discuss helps you stay proactive.
Below are valuable questions to ask your gynecologist, including what to expect during your first visit and how to address reproductive, hormonal, and sexual health topics with confidence.
Gynecological care goes beyond annual exams. It is about understanding your body, your cycles, and the changes that occur through each stage of life. Asking thoughtful questions allows your gynecologist to better guide you, address underlying issues, and help you manage long-term wellness.
Many patients hesitate to ask questions out of embarrassment or uncertainty. However, your gynecologist’s role is to educate, support, and treat without judgment. Open discussions lead to early detection of health concerns, personalized care plans, and reassurance about normal bodily changes.
Here at The Women’s Center, our gynecology specialists value communication as much as medical expertise. We encourage every patient to ask questions that promote clarity and confidence throughout their care journey.
For many women, the first gynecology appointment can feel unfamiliar. If you are a teen, young adult, or visiting after years without care, this visit sets the tone for your relationship with your provider.
Below are key questions to ask your gynecologist on your first visit that can help you better understand your health and what to expect moving forward.
It helps to know what each part of the exam involves. A standard visit may include a pelvic exam, breast exam, Pap test, and discussion of your medical history. Your provider can explain the purpose of each step and address any discomfort or anxiety you might feel.
Frequency depends on your age, symptoms, and previous test results. Regular visits are important for preventive screenings and early detection of conditions like cervical cancer or infections.
Pap smears and HPV tests are central to cervical cancer prevention. Your gynecologist can recommend when to start, how often to repeat them, and what abnormal results mean.
Understanding how to prepare helps you get the most from your appointments. Some questions, such as menstrual tracking or changes in discharge, are easier to answer when you keep a record of your symptoms.
Menstrual cycles reveal much about your reproductive and hormonal balance. Changes in flow, length, or pain intensity can signal underlying conditions such as fibroids, endometriosis, or hormonal fluctuations.
Here are practical questions to ask your gynecologist about your menstrual health:
While every woman’s cycle is unique, there are general signs of a normal period such as predictable timing, moderate bleeding, and minimal discomfort. Asking this question helps you identify what is typical for your body.
Irregular or heavy bleeding may result from stress, hormonal imbalance, thyroid issues, or uterine conditions. Your doctor can evaluate these changes and suggest further testing or treatment options.
Menstrual cramps can range from mild to severe. If pain interferes with your daily life, ask about treatment options such as hormonal therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or lifestyle adjustments.
Hormonal birth control methods often help balance irregular cycles or reduce menstrual pain. Your gynecologist can explain which type may be most effective and suitable for your health history.
Excessive bleeding can lead to anemia or signal uterine fibroids. If you frequently change pads or tampons within an hour, it is important to mention this to your provider for evaluation.
Asking these questions encourages you to pay attention to subtle changes and respond early before symptoms progress into more complex conditions.
Reproductive health involves much more than pregnancy. It also includes understanding ovulation, hormone balance, and long-term wellness. Your gynecologist can guide you through each phase of fertility, from planning conception to managing concerns that may affect it.
Tracking ovulation helps you understand your fertility window and hormonal rhythm. Your gynecologist can explain natural signs of ovulation and recommend reliable tracking methods.
Infertility can be emotionally challenging, but it is often treatable. Your provider may suggest blood tests, imaging studies, or a referral to a fertility specialist to explore possible causes.
Conditions such as pelvic inflammatory disease or fibroid surgery can impact fertility. Discussing your medical history allows your doctor to assess potential risks and recommend preventive care.
Fertility gradually declines with age, particularly after 35. Asking about your current reproductive health helps you plan for family goals or identify options like egg preservation.
Diet, exercise, and stress can influence hormonal balance and reproductive function. A gynecologist can suggest practical ways to support your fertility through everyday habits.
Your reproductive health journey is deeply personal. Open discussions help you make choices that align with your values, goals, and long-term wellness.
Sexual health is a key part of overall well-being, yet many women hesitate to discuss it. Open conversations about intimacy, discomfort, and libido can reveal treatable conditions and help restore confidence in your body.
Below are meaningful questions to ask your gynecologist about sexual health and related changes that may occur with age, hormones, or emotional stress.
Pain during intercourse can stem from dryness, infection, hormonal changes, or pelvic floor disorders. Discussing these symptoms helps your gynecologist identify the cause and recommend effective solutions.
Many factors such as stress, medications, and hormonal changes can affect libido. Your doctor can help determine if these changes are temporary or related to menopause or underlying conditions.
Vaginal dryness becomes common with declining estrogen levels, especially after menopause. Your gynecologist can recommend lubricants, moisturizers, or low-dose estrogen therapy to restore comfort.
Regular STI screening is important for sexually active women at any age. Ask how often you should be tested and what preventive measures such as vaccines or barrier protection are appropriate for you.
Discussing sexual health builds understanding and trust. These conversations also help normalize topics that many women feel hesitant to bring up during appointments.
Menopause brings many physical and emotional transitions. Understanding these changes early helps you manage symptoms and maintain a healthy lifestyle. A conversation with a menopause specialist can offer valuable insight into what to expect and how to cope effectively.
Here are some of the most relevant questions to ask your gynecologist during this stage:
Hot flashes, night sweats, mood shifts, and sleep changes are common during this time. Ask how these symptoms might affect your body and when to consider treatment options.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may relieve hot flashes and prevent bone loss. Your doctor can discuss its benefits, risks, and alternatives such as lifestyle changes or non-hormonal medications.
Falling estrogen levels can affect bone density and cardiovascular health. Your gynecologist may suggest dietary adjustments, exercise routines, and screenings that support long-term wellness.
Discussing these topics helps you approach menopause with clarity instead of uncertainty. Each woman’s experience is different, but knowledge makes the journey smoother.
Your gynecologist is focused on reproductive health. They also play a key role in your overall wellness by tracking how hormonal, physical, and emotional health connect and change over time. These discussions help detect changes early and support long-term balance.
Below are additional questions to ask your gynecologist that extend beyond reproductive care.
Screening recommendations depend on age, family history, and risk factors. Ask your gynecologist when to schedule Pap smears, mammograms, and colon cancer screenings.
After menopause, bone loss can accelerate. Your gynecologist may suggest bone density testing and lifestyle steps to strengthen bone health through diet and exercise.
Hormonal changes can influence mood, anxiety, and sleep. Discuss symptoms such as irritability or fatigue to explore possible links and treatment options.
Balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and sleep hygiene help maintain hormonal health. Your gynecologist can guide you on diet or movement patterns that fit your stage of life.
Even as you approach menopause, tracking your cycle helps spot irregularities that might indicate hormonal shifts or conditions such as fibroids or endometriosis.
Adolescents should schedule their first visit between ages 13 and 15, typically focusing on conversation rather than examination, to build trust and understanding early.
Gynecologists can review which vaccines such as HPV, flu, or Tdap are relevant to your age and risk level. Vaccination plays an important role in preventive care.
Pelvic floor exercises, hydration, and regular screenings support comfort and function. Your gynecologist can recommend therapies for dryness, incontinence, or discomfort.
Taking time to discuss these questions transforms your annual exam into a full wellness check-in, helping you stay proactive and informed at every stage.
Here at The Women’s Center, we welcome every woman to speak openly about her health, concerns, and goals. Our experienced gynecology and menopause specialists support you through each stage of life with understanding and respect.
We take the time to explain, educate, and guide you toward better wellness because your confidence and comfort matter most to us.

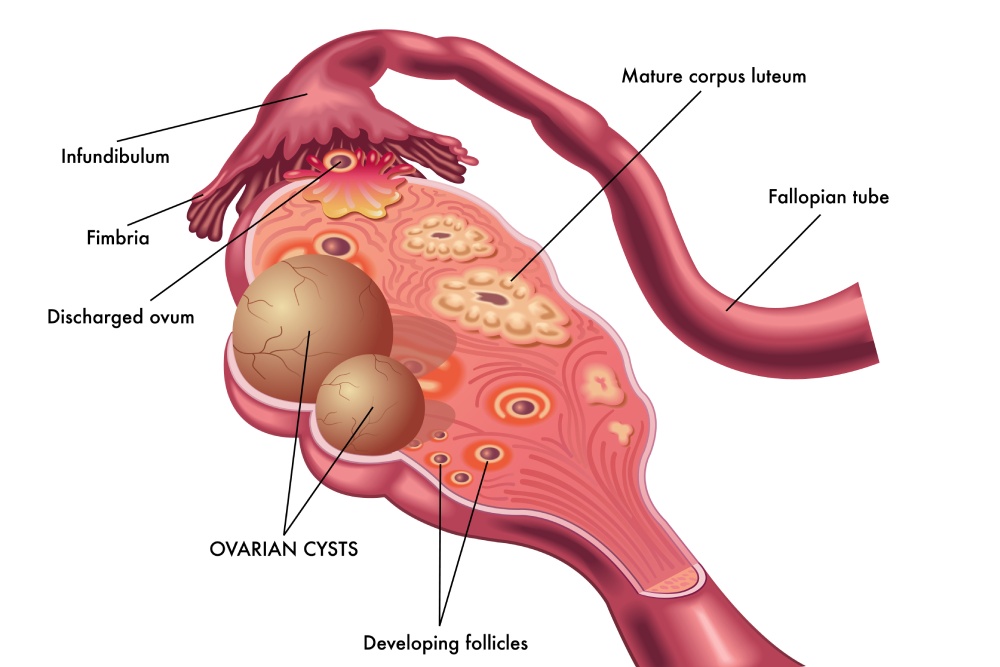


Polycystic Ovary Syndrome affects millions of women worldwide, often bringing challenges like irregular periods, hormonal...
Read More
Ovarian cysts after menopause may seem uncommon, but they can still develop even when the...
Read More
Uterine fibroids are one of the most common benign growths affecting women. By age 50,...
Read More