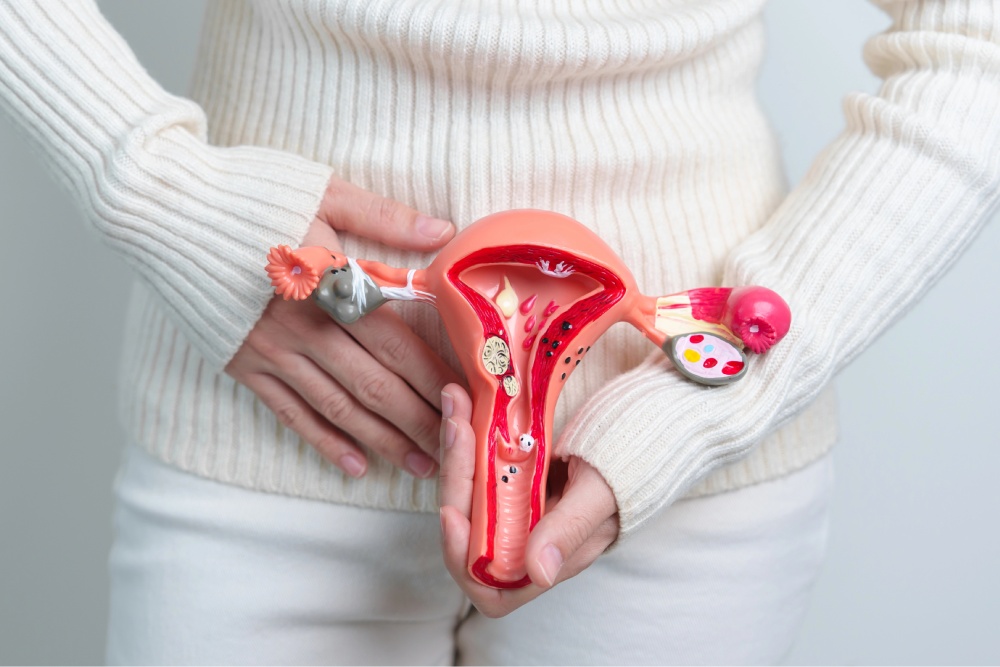
Surgical Solutions: Exploring Hysterectomy As A PCOS Treatment
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome affects millions of women worldwide, often bringing challenges like irregular periods, hormonal...
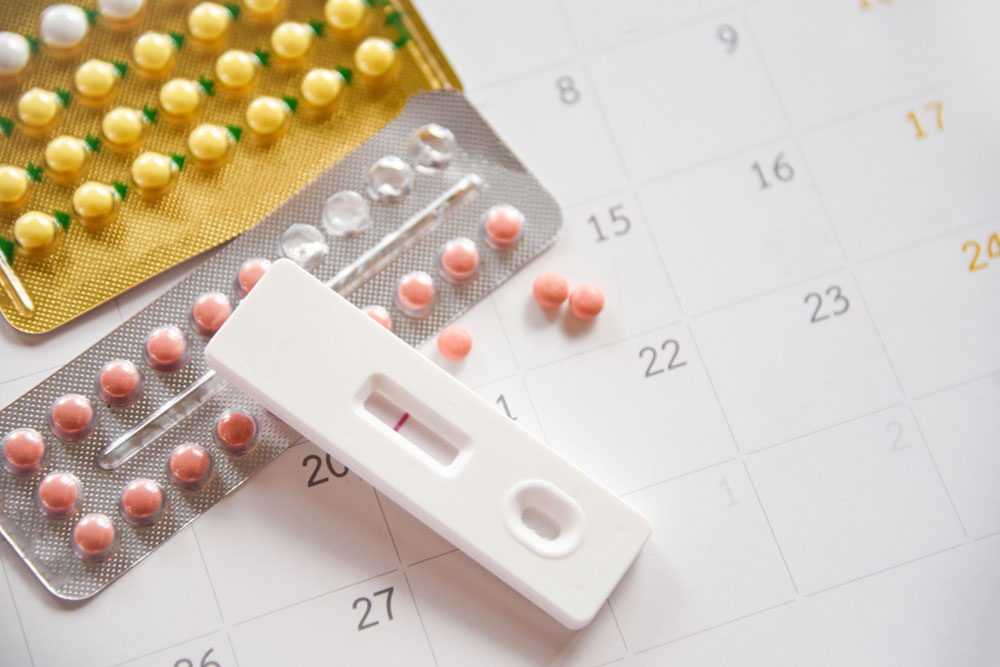
Read MoreFor many women, birth control offers the dual benefits of preventing pregnancy and regulating menstrual cycles. However, it's not uncommon to experience a late period while on birth control. This can lead to anxiety and confusion, especially if you are diligent about taking your contraceptives.
In this article, we will explore how late a period can be on birth control and delve into the possible reasons for this phenomenon.
One of the primary reasons for a late period on birth control is the adjustment period your body undergoes when starting or changing birth control methods. Hormonal contraceptives, including pills, patches, rings, and IUDs, work by altering the hormonal balance in your body to prevent ovulation.
When you switch from one form of birth control to another, your body needs time to adapt to the new hormone levels. This adjustment can cause your period to be delayed or missed altogether. It's important to follow your healthcare provider's advice when transitioning between birth control methods to ensure continuity of contraception and to manage expectations around menstrual changes.
Stress is a significant factor that can disrupt menstrual cycles, even for those on birth control. The hypothalamus, a part of the brain responsible for regulating hormones that control the menstrual cycle, can be affected by stress.
High stress levels can lead to an increase in cortisol, a hormone that can interfere with the normal hormonal signals that trigger menstrual bleeding.
This disruption can result in a delayed or missed period. Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, adequate sleep, and physical activity can help restore regularity to your cycle.
Intense physical exercise can also be a culprit in causing late periods on birth control. Engaging in high levels of physical activity can raise cortisol levels, similar to stress, affecting hormonal balance.
Additionally, significant changes in diet, particularly inadequate caloric intake, can lead to missed periods. When your body doesn't get enough calories to sustain its activities, it may halt non-essential functions, including ovulation and menstruation, to conserve energy.
Ensuring you consume enough calories to meet your energy needs is crucial for maintaining a regular menstrual cycle.
Several underlying health conditions can cause irregular periods, including polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and hormonal imbalances. PCOS, for instance, leads to the production of excess androgen hormones, which can interfere with the normal menstrual cycle and cause delayed periods.
Thyroid disorders, whether an overactive or underactive thyroid, can also disrupt the balance of hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular or missed periods. If you suspect that an underlying health condition is affecting your menstrual cycle, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate management.
Certain medications can affect your menstrual cycle, including those not directly related to birth control. Antidepressants, antipsychotics, and medicines for epilepsy can interfere with hormonal balance and delay your period.
If you start a new medication and notice changes in your menstrual cycle, it's worth discussing with your healthcare provider to determine if the medication could be the cause. Your provider may need to adjust your medication or offer alternative solutions to manage the side effects.
Although birth control is highly effective at preventing pregnancy, no method is foolproof. If you miss your period and are sexually active, there is a possibility of pregnancy, particularly if you've missed doses or have not been consistent with your birth control.
Taking an at-home pregnancy test can clarify and help you take the next steps. Consistent and correct use of birth control is essential to maintain its effectiveness and prevent unintended pregnancy.
If you experience a late period while on birth control, it's generally not a cause for immediate concern. However, if you miss three or more periods in a row, experience significant changes in menstrual bleeding, or have symptoms of hormonal imbalance, it's important to seek medical advice.
Persistent irregularities in your menstrual cycle could indicate an underlying health issue that needs to be addressed. Your healthcare provider can perform a thorough assessment and recommend the appropriate action to restore regularity to your cycle.
If you're experiencing irregular periods or have concerns about your menstrual health, contact us at The Women's Center. Our team of healthcare professionals is dedicated to providing comprehensive care and personalized solutions to support your well-being. Book an appointment today to discuss your symptoms and get your needed care.

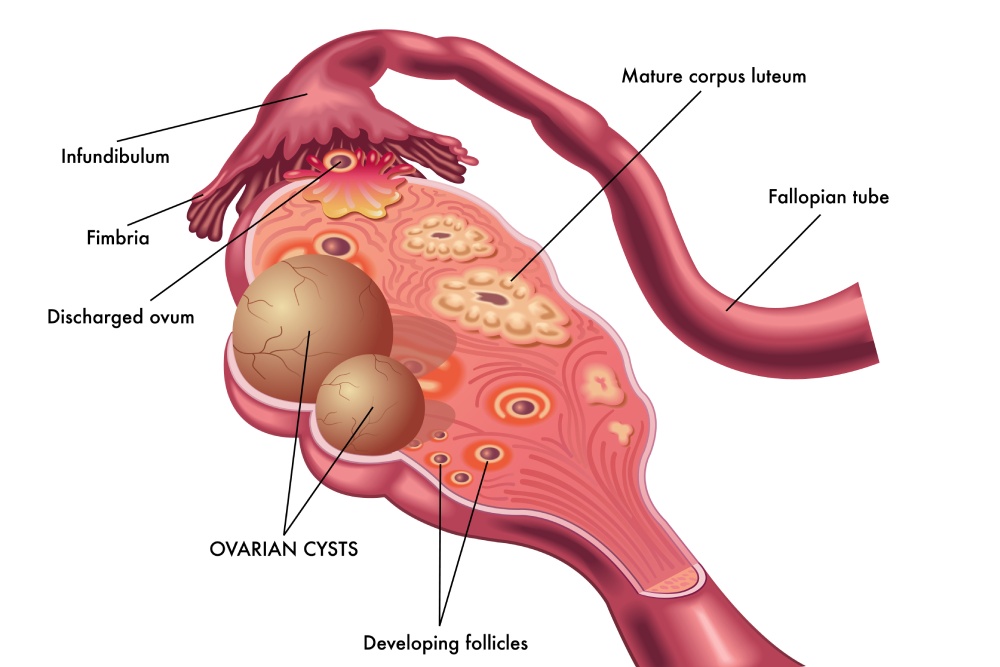


Polycystic Ovary Syndrome affects millions of women worldwide, often bringing challenges like irregular periods, hormonal...
Read More
Ovarian cysts after menopause may seem uncommon, but they can still develop even when the...
Read More
Uterine fibroids are one of the most common benign growths affecting women. By age 50,...
Read More